- Like
- SHARE
- Digg
- Del
- Tumblr
- VKontakte
- Flattr
- Buffer
- Love This
- Save
- Odnoklassniki
- Meneame
- Blogger
- Amazon
- Yahoo Mail
- Gmail
- AOL
- Newsvine
- HackerNews
- Evernote
- MySpace
- Mail.ru
- Viadeo
- Line
- Comments
- Yummly
- SMS
- Viber
- Telegram
- JOIN
- Skype
- Facebook Messenger
- Kakao
- LiveJournal
- Yammer
- Edgar
- Fintel
- Mix
- Instapaper
- Copy Link
Introduction
Diabetes is a common name for a group of chronic endocrine diseases. All diseases of this group have a common symptom, polyuria (increased urine formation). But diabetes is associated with an increased concentration of glucose in the blood. We will tell you more about this disease.
If you need diabetes medication, you can find it on PillPal but remember that your health is the most precious thing you have and you are responsible for it. So be 100% sure about the medications you purchase. Self-treatment without proper knowledge and experience can harm you.
Types of Diabetes
Diabetes mellitus, an endocrine disorder caused by violation of metabolic processes in the body, is the most common. Its main symptom is hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) caused by insulin deficiency.
But there are also other types:
- Diabetes insipidus – It’s caused by the resistance of the body to vasopressin, a peptide hormone of the hypothalamus responsible for fluid retention in the body
- Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus – It is characterized by a loss of the ability to concentrate urine. The hereditary type is caused by genetic mutations. The acquired one is caused by renal diseases or abnormalities in the brain
All these diseases are accompanied by a large loss of fluid and impaired mineral metabolism. Insipidus diabetes is not life-threatening if patients adequately quench their thirst in time.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most pressing global health problems. According to WHO, it affects about 500 million people worldwide.
This disease is characterized by multiple metabolic disorders of:
- glucose regulation
- protein metabolism
- carbohydrate metabolism
- lipid metabolism
- the water-salt balance
- mineral metabolism
Insulin, a protein-peptide hormone of the pancreas, plays the main role in the development of this pathology. It’s responsible for maintaining normal blood glucose levels, ensuring its flow to tissue cells for their nutrition. Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder. Depending on the type of the disease, either the pancreas does not produce enough insulin, or the body loses sensitivity to it. As a result, glucose does not reach the cells but accumulates in the blood. Tissues experience energy starvation.
Symptoms of Diabetes
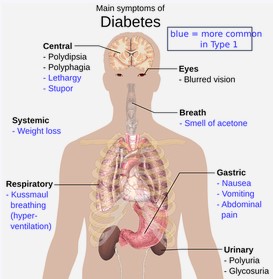 Both types of this disease are characterized by frequent hunger pangs, constant thirst, and frequent urination. All of these are signs of hyperglycemia. This means that the patient has a lot of sugar in their blood.
Both types of this disease are characterized by frequent hunger pangs, constant thirst, and frequent urination. All of these are signs of hyperglycemia. This means that the patient has a lot of sugar in their blood.
Diabetes mellitus is also accompanied by these symptoms:
- visual impairment
- numbness of the extremities
- increased sweating
- increased fatigue
- muscle weakness
- long healing of wounds
- skin itching
In type 1 diabetes, bedwetting is possible. Type 2 diabetes is also accompanied by black acanthosis (dark skin thickening on the neck, armpits, groin, and elbows). Insulin inhibits the breakdown of adipose tissue. Therefore, patients with type 2 diabetes suffer from excessive weight because of insulin resistance. The first type can provoke rapid weight loss because of cellular starvation.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Depending on the reason why glucose transport is impaired, there are the following types of diabetes mellitus:
- Type 1 diabetes – It is caused by insulin deficiency. The pancreas fails, so the patient needs to take medications containing this hormone
- Type 2 diabetes – It is caused by insulin resistance. The hormone is sufficient in the body but the cells are insensitive to it so glucose transport does not occur
- Gestational diabetes – It develops during pregnancy and threatens the health of the mother and child
A pre-diabetic condition is characterized by reduced glucose tolerance. Sugar remains within normal limits on an empty stomach but an abnormality is detected after a glucose load.
Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity
Scientists have identified a relationship between diabetes mellitus and being overweight. Insulin prevents the breakdown of fat, making weight loss almost impossible for the patient but obesity complicates the course of the disease:
- fat is deposited in the abdominal area
- the pancreas and liver are compressed
- the carbohydrate-lipid metabolism is disturbed
- insulin production is activated
- insulin sensitivity decreases
Visceral obesity can be resulted from a sedentary lifestyle and excessive androgens (male hormones), and can also be inherited. According to the standards of the World Organization of Gastroenterology, it is diagnosed when the waist circumference is more than 31 inches in women and 37 cm in men. The National Cholesterol Education Program also focuses on the ratio of waist to hip circumference: more than 0.85 in women and 0.9 in men.
Risk Group
Patients who are overweight or have polycystic ovarian syndrome have a higher chance of getting diabetes. At risk are also people who are:
- over 45 years of age
- having diabetes parents
- suffering from arterial hypertension
- having a sedentary lifestyle
- deprived of breastfeeding in childhood
- eating many carbohydrates and fats
- smokers
Reduced glucose tolerance is also a reason to monitor your health more closely. Diabetes mellitus can occur more than 10 years after diagnosis of prediabetes. At the same time, the disease may not be diagnosed due to its mild symptoms in its early stage.
You may also like…
About Theresa Duncan
Originally from Detroit, MI, Theresa has been offering health and fitness advice for the last 30 years while working as an engineer. She decided to turn her passion into a profession, and finds nothing more satisfying than helping others reach their health and fitness goals.

